Developing for Hog¶
Become a member of the Hog community¶
To become a Hog developer, get in contact with one of us (e.g. Francesco Gonnella or Davide Cieri), such that we can have a quick feedback of your background and your expertise.
Developing for Hog¶
As a Hog developer, please follow these instructions:
go to Hog on gitlab
check in the issues list that your improvements/features are not already under development.
create a new issue by clicking on “New issue” button
use a meaningful short name
write a comprehensive description of the changes you plan to make
the issue must be assigned to you
use labels to indicate whether it is a new feature a bug-fix, etc
(OPTIONAL) use due date to indicate when you expect to conclude your work
open a new merge request
starting from your newly created issue
expand Merge Request drop-down
expand Create Merge Request
direct your merge request to
developbranchbranch name: feature/<issue_short_name>
click on “Create Merge Request”:
a new merge request is created
the merge request will be marked as Draft
a new development branch is created
clone the TestFirmware repository
cd path_to_workdir/ git clone --recursive https://gitlab.cern.ch/hog/test/TestFirmware.git
Create a new branch in the test firmware repository with the same name as the one in the main Hog repository
cd path_to_workdir/TestFirmware/ git checkout -b feature/<issue_short_name>
Move Hog to your branch
cd path_to_workdir/TestFirmware/Hog/ git checkout feature/<issue_short_name>
Develop a test for your new feature before writing your code
eventually modify an existing tests
commit your tests
cd path_to_workdir/TestFirmware/ git commit <test1> <test1> <...> -m "Adding tests for feature/<issue_short_name>: <brief_test_description>"
Develop the code for the new feature (in this order)
all code must be documented using doxygen comments in the code!
commit your code
cd path_to_workdir/TestFirmware/Hog/ git commit <file1> <file2> <...> -m "Working on feature/<issue_short_name>: <brief_commit_description>"
Test your code
all your new test must succeed
all existing test must succeed
if the test fails, fix your code and commit it using –amend
cd path_to_workdir/TestFirmware/Hog/ git commit --amend --no-edit
If your modification has any impact on the user/maintainer part, update the user manual accordingly
Push your changes in the Hog repository
cd path_to_workdir/TestFirmware/Hog/ git push
Push your changes on the TestFirmware repository
cd path_to_workdir/TestFirmware/ git push --set-upstream origin feature/<issue_short_name>
Remove Draft status from your Merge Request - go to Hog on gitlab - navigate to your merge request - click on “Mark as Ready” button
Drop us a line at Hog support or on the Mattermost channel
Check your Merge Request and address comments
Documenting the code¶
All the code written to implement new features or correct bugs must be documented. The main source of documentation is doxygen and comments in the code. The doxygen documentation is collected in a dedicated website
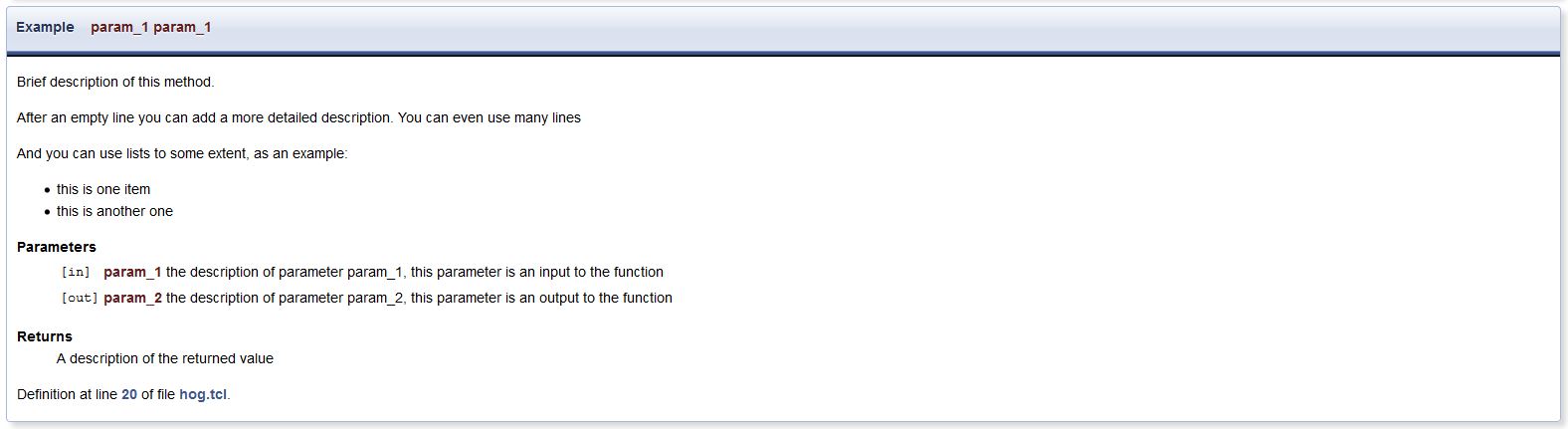
An example of how to document new functions
# @brief Brief description of this method
#
# After an empty line you can add a more detailed description.
# You can even use many lines
#
# @param[in] param_1 the description of parameter param_1, this parameter is an input to the function
# @param[out] param_2 the description of parameter param_2, this parameter is an output to the function
#
# @returns A description of the returned value
#
proc Example {param_1 param_1} {
if {[info commands get_property] != ""} {
# some Vivado specific comments that will not end up in the documentation
return "Vivado"
} elseif {[info commands quartus_command] != ""} {
# some Vivado specific comments that will not end up in the documentation
return "Quartus"
} else {
# Tcl Shell
return "DEBUG_propery_value"
}
}
The resulting documentation will be a brief description in the list of available functions:

Linked to a detailed description:
The same comment style can be used also for bash scripts provided you use functions in your script.
Contributing to the Manual¶
This site uses MkDocs to render the Markdown files. The source is hosted on Gitlab: Hog
To contribute to the user manual please read this section carefully. You should first clone the repository:
git clone https://gitlab.cern.ch/hog/hog-docs
As an alternative you can use the Web IDE directly from the Gitlab website. This allows you to preview the resulting page.
If you want to do this locally and haven’t set up your permissions for local Gitlab yet, follow the instructions here.
Everything you’ll need to edit is inside the docs/ directory.
Sections are represented by subdirectories within docs/ while the “Introduction” section comes from index.md.
You can create further markdown files to add topics to the section.
Any change you make in the repository is propagated to the website, when you push your commits into the master branch.
